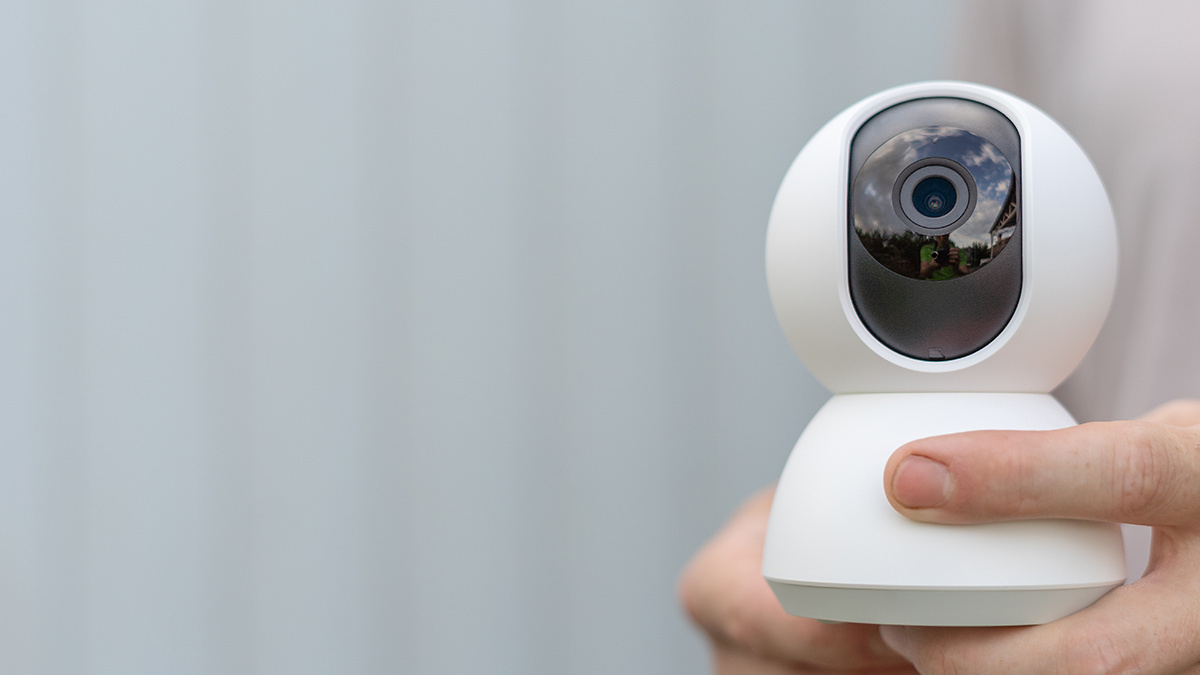
A zero-click vulnerability in a popular IoT security camera could allow an unauthenticated attacker to gain full access to the device and possibly internal networks, a researcher has warned.
The researcher, dubbed ‘Watchful IP’, has released details of the unauthenticated remote code execution (RCE) bug in certain products from Hikvision, a Chinese manufacturer and world’s biggest network camera brand.
In a blog post, they described how the security vulnerability, tracked as CVE-2021-36260, could enable a malicious actor to completely takeover an internet-connected camera and potentially internal networks.
The critical bug – awarded 9.8 on the CVSS scale of severity – enables the actor to gain “far more access than even the owner of the device has as they are restricted to a limited ‘protected shell’ (psh) which filters input to a predefined set of limited, mostly informational commands”, Watchful IP explained.
“In addition to complete compromise of the IP camera, internal networks can then be accessed and attacked.
“This is the highest level of critical vulnerability – a zero click unauthenticated remote code execution (RCE) vulnerability affecting a high number of Hikvision cameras.”
They added: “Given the deployment of these cameras at sensitive sites potentially even critical infrastructure is at risk.”
Long-standing bug
The researcher claims that firmware has been susceptible to the bug since as far back as 2016.
Hikvision has acknowledged the findings and has patched the issue. The company has also released a security advisory detailing which products are at risk.
A summary reads: “Due to the insufficient input validation, attacker can exploit the vulnerability to launch a command injection attack by sending some messages with malicious commands.”
The advisory also contains an extensive list of vulnerable versions.
The Daily Swig has reached out to the researcher for more information and will update this article accordingly.



























You must be logged in to post a comment Login