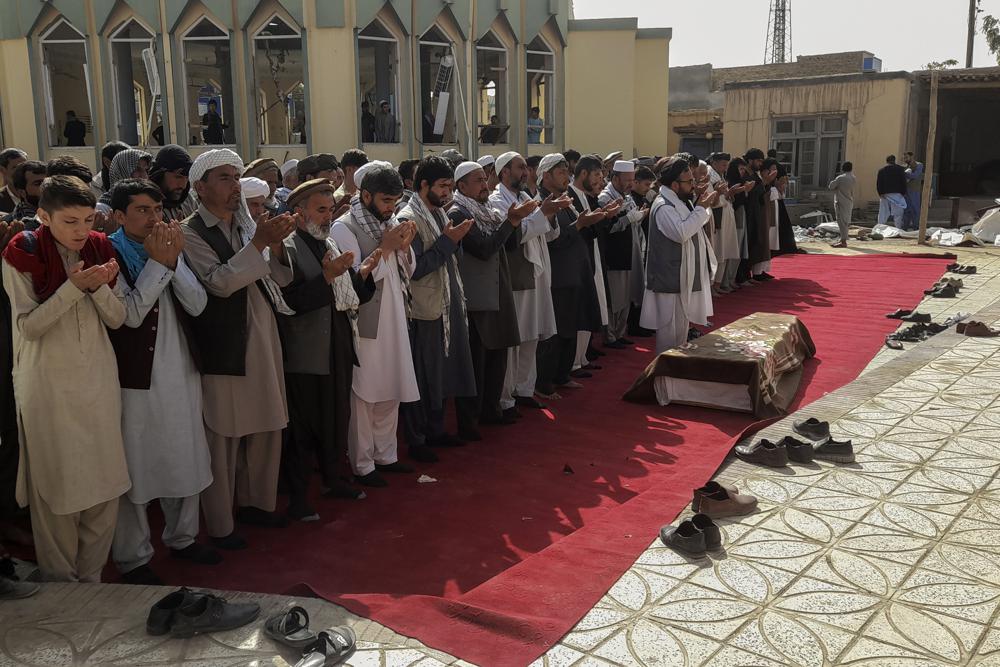
Relatives and residents pray during a funeral ceremony for victims of a suicide attack at the Gozar-e-Sayed Abad Mosque in Kunduz, northern Afghanistan, Saturday, Oct. 9, 2021. The mosque was packed with Shiite Muslim worshippers when an Islamic State suicide bomber attacked during Friday prayers, killing dozens in the latest security challenge to the Taliban as they transition from insurgency to governance. (AP Photo/Abdullah Sahil)
ISLAMABAD (AP) — The Taliban on Saturday ruled out cooperation with the United States to contain extremist groups in Afghanistan, staking out an uncompromising position on a key issue ahead of the first direct talks between the former foes since America withdrew from the country in August.
Senior Taliban officials and U.S. representatives are meeting this weekend in Doha, the capital of Qatar. Officials from both sides have said issues include reining in extremist groups and the evacuation of foreign citizens and Afghans from the country. The Taliban have signaled flexibility on evacuations.
However, Taliban political spokesman Suhail Shaheen told The Associated Press there would be no cooperation with Washington on containing the increasingly active Islamic State group in Afghanistan. IS has taken responsibility for a number of recent attacks, including a suicide bombing Friday that killed 46 minority Shiite Muslims and wounded dozens as they prayed in a mosque in the northern city of Kunduz.
“We are able to tackle Daesh independently,” Shaheen said, when asked whether the Taliban would work with the U.S. to contain the Islamic State affiliate. He used an Arabic acronym for IS.
IS has carried out relentless assaults on the country’s Shiites since emerging in eastern Afghanistan in 2014. It is also seen as the terror group that poses the greatest threat to the United States for its potential to stage attacks on American targets.
The weekend meetings in Doha are the first since U.S. forces withdrew from Afghanistan in late August, ending a 20-year military presence as the Taliban overran the country. The U.S. has made it clear the talks are not a preamble to recognition.
The talks also come on the heels of two days of difficult discussions between Pakistani officials and U.S. Deputy Secretary of State Wendy Sherman in Islamabad that focused on Afghanistan. Pakistani officials urged the U.S. to engage with Afghanistan’s new rulers and release billions of dollars in international funds to stave off an economic meltdown.
Pakistan also had a message for the Taliban, urging them to become more inclusive and pay attention to human rights and minority ethnic and religious groups.
Later on Saturday, Doha-based Al-Jazeera English reported the talks had kicked off. The news outlet cited Ameer Khan Muttaqi, the Taliban-appointed foreign minister for Afghanistan, as saying the Taliban had asked the U.S. to lift its ban on the reserves of the Afghan central bank.
There was no immediate word from Washington on the talks.
Following Friday’s attack, Afghanistan’s Shiite clerics assailed the Taliban, demanding greater protection at their places of worship. The IS affiliate claimed responsibility and identified the bomber as a Uyghur Muslim. The claim said the attack targeted both Shiites and the Taliban for their purported willingness to expel Uyghurs to meet demands from China. It was the deadliest attack since U.S. and NATO troops left Afghanistan on Aug. 30.
Michael Kugelman, deputy director of the Asia Program at the U.S.-based Wilson Center, said Friday’s attack could be a harbinger of more violence. Most of the Uyghur militants belong to the East Turkestan Islamic Movement, which has found a safe haven in the border regions of Pakistan and Afghanistan for decades.
“If the (IS) claim is true, China’s concerns about terrorism in (Afghanistan)—to which the Taliban claims to be receptive—will increase,” he tweeted following the attack.
Meanwhile, the Taliban on Saturday began busing Afghans who had fled from the insurgents’ blitz takeover in August and were living in tents in a Kabul park back to their homes in the country’s north, where threats from IS are mounting following the Kunduz attack.
A Taliban official in charge of refugees, Mohammed Arsa Kharoti, said there are up to 1.3 million Afghans displaced from past wars and that the Taliban lack funds to organize the return home for all. He said the Taliban have organized the return of 1,005 displaced families to their homes so far.
Shokria Khanm, who had spent several weeks in one of the tents in the park and was waiting Saturday to board the Taliban-organized bus back home to Kunduz, said she isn’t concerned about the growing IS threat in the northern province.
“At least there we have four walls,” she said but added that she was nervous about the future after fighting between the Taliban and Afghan government troops had destroyed her house.
“Winter is on the way. There is no firewood. We need water and food,” she said.
During the Doha talks, U.S. officials will also seek to hold the Taliban to their commitment to allow Americans and other foreign nationals to leave Afghanistan, along with Afghans who once worked for the U.S. military or government and other Afghan allies, a U.S. official said. The official spoke on condition of anonymity because the official was not authorized to speak on the record about the meetings.
The Biden administration has fielded questions and complaints about the slow pace of U.S.-facilitated evacuations from Taliban-ruled Afghanistan since the U.S. withdrawal.
Associated Press writers Ellen Knickmeyer in Washington and Samya Kullab in Kabul, Afghanistan, contributed to this report.
Copyright 2021 Associated Press. All rights reserved.