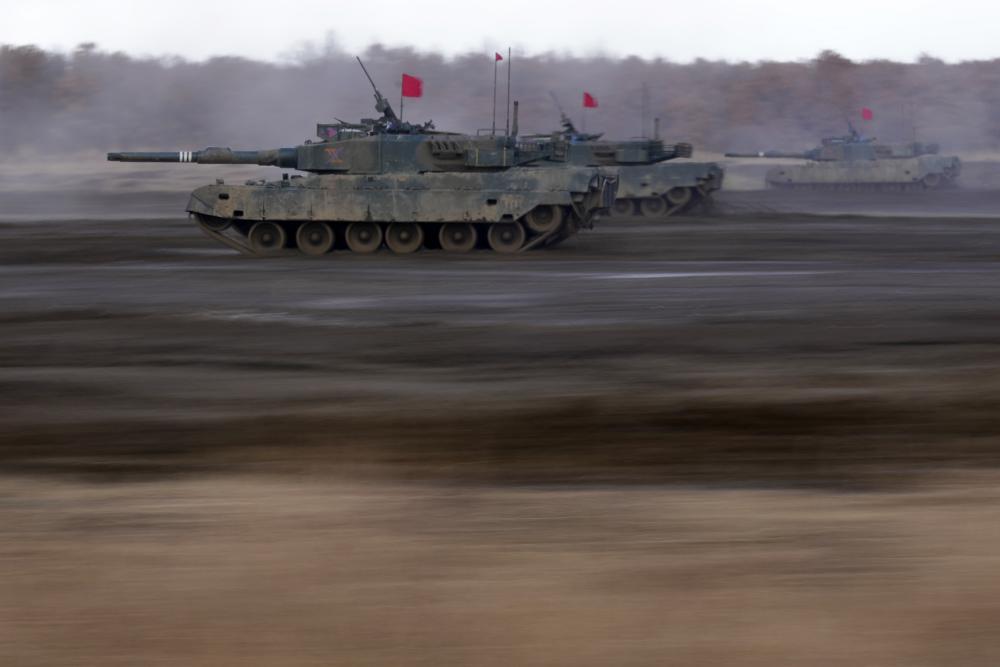
Japanese Ground-Self Defense Force (JGDDF) Type 90 tanks drive toward a target during the annual drill with live ammunitions exercise at Minami Eniwa Camp Monday, Dec. 6, 2021, in Eniwa, northern Japan of Hokkaido. Dozens of tanks are rolling over the next two weeks on Hokkaido, a main military stronghold for a country with perhaps the world’s most little known yet powerful army. (AP Photo/Eugene Hoshiko)
ENIWA, Japan (AP) — Dozens of tanks and soldiers fired explosives and machine guns in drills Monday on Japan’s northern island of Hokkaido, a main stronghold for a nation that is perhaps the world’s least-known military powerhouse.
Just across the sea from rival Russia, Japan opened up its humbly named Self Defense Force’s firing exercises to the media in a display of public firepower that coincides with a recent escalation of Chinese and Russian military moves around Japanese territory.
The drills, which foreign journalists rarely have a chance to witness, will continue for nine days and include about 1,300 Ground Self Defense Force troops. On Monday, as hundreds of soldiers cheered from the sidelines and waved unit flags, lines of tanks shot at targets meant to represent enemy missiles or armored vehicles.
The exercises illuminate a fascinating, easy-to-miss point. Japan, despite an officially pacifist constitution written when memories of its World War II rampage were still fresh — and painful — boasts a military that puts all but a few nations to shame.
And, with a host of threats lurking in Northeast Asia, its hawkish leaders are eager for more.
It’s not an easy sell. In a nation still reviled by many of its neighbors for its past military actions, and where domestic pacifism runs high, any military buildup is controversial.
Japan has focused on its defensive capabilities and carefully avoids using the word “military” for its troops. But as it looks to defend its territorial and military interests against an assertive China, North Korea and Russia, officials in Tokyo are pushing citizens to put aside widespread unease over a more robust role for the military and support increased defense spending.
As it is, tens of billions of dollars each year have built an arsenal of nearly 1,000 warplanes and dozens of destroyers and submarines. Japan’s forces rival those of Britain and France, and show no sign of slowing down in a pursuit of the best equipment and weapons money can buy.
Not everyone agrees with this buildup. Critics, both Japan’s neighbors and at home, urge Tokyo to learn from its past and pull back from military expansion.
There’s also domestic wariness over nuclear weapons. Japan, the only nation to have atomic bombs dropped on it in war, possesses no nuclear deterrent, unlike other top global militaries, and relies on the so-called U.S. nuclear umbrella.
Proponents of the new military muscle flexing, however, say the expansion is well-timed and crucial to the Japanese alliance with Washington.
China and Russia have stepped up military cooperation in recent years in an attempt to counter growing U.S.-led regional partnerships.
In October, a fleet of five warships each from China and Russia circled Japan as they traveled through the Pacific to the East China Sea. Last month, their warplanes flew together near Japan’s airspace, causing Japanese fighter jets to scramble. In fiscal year 2020 through March, Japanese fighters scrambled more than 700 times — two-thirds against Chinese warplanes, with the remainder mostly against Russians — the Defense Ministry said.
Russia’s military also recently deployed coastal defense missile systems, the Bastion, near disputed islands off the northern coast of Hokkaido.
Japan was disarmed after its WW II defeat. But a month after the Korean War began in 1950, U.S. occupation forces in Japan created a 75,000-member lightly armed de facto army called the National Police Reserve. The Self Defense Force, the country’s current military, was founded in 1954.
Today, Japan is ranked fifth globally in overall military power after the United States, Russia, China and India, and its defense budget ranked sixth in the 2021 ranking of 140 countries by the Global Firepower rating site.
During archconservative former Prime Minister Shinzo Abe’s more than eight-year rule, which ended a year ago, Japan significantly expanded its military role and budget. Abe also watered down the war-renouncing Article 9 of the constitution in 2015, allowing Japan to come to the defense of the United States and other partner nations.
Japan has rapidly stepped up its military role in its alliance with Washington, and has made more purchases of costly American weapons and equipment, including fighter jets and missile interceptors.
“Japan faces different risks coming from multiple fronts,” said defense expert Heigo Sato, a professor at the Institute of World Studies at Takushoku University in Tokyo.
Among those risks are North Korea’s increased willingness to test high-powered missiles and other weapons, provocations by armed Chinese fishing boats and coast guard ships, and Russia’s deployment of missiles and naval forces.
One of North Korea’s missiles flew over Hokkaido, landing in the Pacific in 2017. In September, another fell within the 200-nautical mile exclusive economic zone off northwestern Japan.
Under a bilateral security pact, Japan hosts about 50,000 U.S. troops, mostly on the southern island of Okinawa, which, along with Japanese units in Hokkaido, are strategically crucial to the U.S. presence in the Pacific.
Japanese Prime Minister Fumio Kishida, who took office in October, said during his first troop review that he would consider “all options,” including possibly pursuing pre-emptive strike capabilities to further “increase Japan’s defense power” — a divisive issue that opponents say violates the constitution.
Japan has more than 900 warplanes, 48 destroyers, including eight Aegis missile-combating systems, and 20 submarines. That exceeds Britain, Germany and Italy. Japan is also buying 147 F-35s, including 42 F-35Bs, making it the largest user of American stealth fighters outside of the United States, where 353 are to be deployed.
Their deployment is crucial for Japanese defense in the Indo-Pacific, and the country is now retrofitting two flattops, the Izumo and Kaga, as the country’s first aircraft carriers since the end of the World War II.
Among Japan’s biggest worries is China’s increased naval activity, including an aircraft carrier that has been repeatedly spotted off Japan’s southern coasts.
Japan has customarily maintained a defense budget cap at 1% of its GDP, though in recent years the country has faced calls from Washington to spend more.
Kishida says he is open to doubling the cap to the NATO standard of 2%.
As a first step, his Cabinet recently approved a 770 billion yen ($6.8 billion) extra budget for the fiscal year to accelerate missile defense and reconnaissance activity around Japanese territorial seas and airspace, and to bolster mobility and emergency responses to defend its remote East China Sea islands. That would bring the 2021 defense spending total to 6.1 trillion yen ($53.2 billion), up 15% from the previous year, and 1.09% of Japan’s GDP.
Experts say a defense budget increase is the price Japan must pay now to make up for a shortfall during much of the postwar era, when the country prioritized economic growth over national security.
As China is playing tough in the Asia-Pacific region, Taiwan has emerged as a regional flashpoint, with Japan, the United States and other democracies developing closer ties with the self-ruled island that Beijing regards as a renegade territory to be united by force if necessary.
China’s buildup of military facilities in the South China Sea has heightened Tokyo’s concerns in the East China Sea, where the Japanese-controlled Senkaku islands are also claimed by Beijing, which calls them Diaoyu. China has sent a fleet of armed coast guard boats to routinely circle them and to go in and out of Japanese-claimed waters, sometimes chasing Japanese fishing boats in the area.
Japan deploys PAC3 land-to-air missile interceptors on its westernmost island of Yonaguni, which is only 110 kilometers (68 miles) east of Taiwan.
In part because of a relative decline of America’s global influence, Japan has expanded military partnerships and joint exercises beyond its alliance with the United States, including with Australia, Canada, Britain, France and other European countries, as well as in the Association of Southeast Asian Nations. Japan also cooperates with NATO.
Despite the government’s argument that more is needed, there are worries domestically over Japan’s rapid expansion of defense capabilities and costs.
“Although the defense policy needs to respond flexibly to changes in the national security environment, a soaring defense budget could cause neighboring countries to misunderstand that Japan is becoming a military power and accelerate an arms race,” the newspaper Tokyo Shimbun said in a recent editorial.
In October, a fleet of five warships each from China and Russia circled Japan as they traveled through the Pacific to the East China Sea. Last month, their warplanes flew together near Japan’s airspace, causing Japanese fighter jets to scramble. In fiscal year 2020 through March, Japanese fighters scrambled more than 700 times — two-thirds against Chinese warplanes, with the remainder mostly against Russians — the Defense Ministry said.
Russia’s military also recently deployed coastal defense missile systems, the Bastion, near disputed islands off the northern coast of Hokkaido.
Japan was disarmed after its WW II defeat. But a month after the Korean War began in 1950, U.S. occupation forces in Japan created a 75,000-member lightly armed de facto army called the National Police Reserve. The Self Defense Force, the country’s current military, was founded in 1954.
Today, Japan is ranked fifth globally in overall military power after the United States, Russia, China and India, and its defense budget ranked sixth in the 2021 ranking of 140 countries by the Global Firepower rating site.
During archconservative former Prime Minister Shinzo Abe’s more than eight-year rule, which ended a year ago, Japan significantly expanded its military role and budget. Abe also watered down the war-renouncing Article 9 of the constitution in 2015, allowing Japan to come to the defense of the United States and other partner nations.
Japan has rapidly stepped up its military role in its alliance with Washington, and has made more purchases of costly American weapons and equipment, including fighter jets and missile interceptors.
“Japan faces different risks coming from multiple fronts,” said defense expert Heigo Sato, a professor at the Institute of World Studies at Takushoku University in Tokyo.
Among those risks are North Korea’s increased willingness to test high-powered missiles and other weapons, provocations by armed Chinese fishing boats and coast guard ships, and Russia’s deployment of missiles and naval forces.
One of North Korea’s missiles flew over Hokkaido, landing in the Pacific in 2017. In September, another fell within the 200-nautical mile exclusive economic zone off northwestern Japan.
Under a bilateral security pact, Japan hosts about 50,000 U.S. troops, mostly on the southern island of Okinawa, which, along with Japanese units in Hokkaido, are strategically crucial to the U.S. presence in the Pacific.
Japanese Prime Minister Fumio Kishida, who took office in October, said during his first troop review that he would consider “all options,” including possibly pursuing pre-emptive strike capabilities to further “increase Japan’s defense power” — a divisive issue that opponents say violates the constitution.
Japan has more than 900 warplanes, 48 destroyers, including eight Aegis missile-combating systems, and 20 submarines. That exceeds Britain, Germany and Italy. Japan is also buying 147 F-35s, including 42 F-35Bs, making it the largest user of American stealth fighters outside of the United States, where 353 are to be deployed.
Their deployment is crucial for Japanese defense in the Indo-Pacific, and the country is now retrofitting two flattops, the Izumo and Kaga, as the country’s first aircraft carriers since the end of the World War II.
Among Japan’s biggest worries is China’s increased naval activity, including an aircraft carrier that has been repeatedly spotted off Japan’s southern coasts.
Japan has customarily maintained a defense budget cap at 1% of its GDP, though in recent years the country has faced calls from Washington to spend more.
Kishida says he is open to doubling the cap to the NATO standard of 2%.
As a first step, his Cabinet recently approved a 770 billion yen ($6.8 billion) extra budget for the fiscal year to accelerate missile defense and reconnaissance activity around Japanese territorial seas and airspace, and to bolster mobility and emergency responses to defend its remote East China Sea islands. That would bring the 2021 defense spending total to 6.1 trillion yen ($53.2 billion), up 15% from the previous year, and 1.09% of Japan’s GDP.
Experts say a defense budget increase is the price Japan must pay now to make up for a shortfall during much of the postwar era, when the country prioritized economic growth over national security.
As China is playing tough in the Asia-Pacific region, Taiwan has emerged as a regional flashpoint, with Japan, the United States and other democracies developing closer ties with the self-ruled island that Beijing regards as a renegade territory to be united by force if necessary.
China’s buildup of military facilities in the South China Sea has heightened Tokyo’s concerns in the East China Sea, where the Japanese-controlled Senkaku islands are also claimed by Beijing, which calls them Diaoyu. China has sent a fleet of armed coast guard boats to routinely circle them and to go in and out of Japanese-claimed waters, sometimes chasing Japanese fishing boats in the area.
Japan deploys PAC3 land-to-air missile interceptors on its westernmost island of Yonaguni, which is only 110 kilometers (68 miles) east of Taiwan.
In part because of a relative decline of America’s global influence, Japan has expanded military partnerships and joint exercises beyond its alliance with the United States, including with Australia, Canada, Britain, France and other European countries, as well as in the Association of Southeast Asian Nations. Japan also cooperates with NATO.
Despite the government’s argument that more is needed, there are worries domestically over Japan’s rapid expansion of defense capabilities and costs.
“Although the defense policy needs to respond flexibly to changes in the national security environment, a soaring defense budget could cause neighboring countries to misunderstand that Japan is becoming a military power and accelerate an arms race,” the newspaper Tokyo Shimbun said in a recent editorial.
Copyright 2021 Associated Press. All rights reserved.




























You must be logged in to post a comment Login