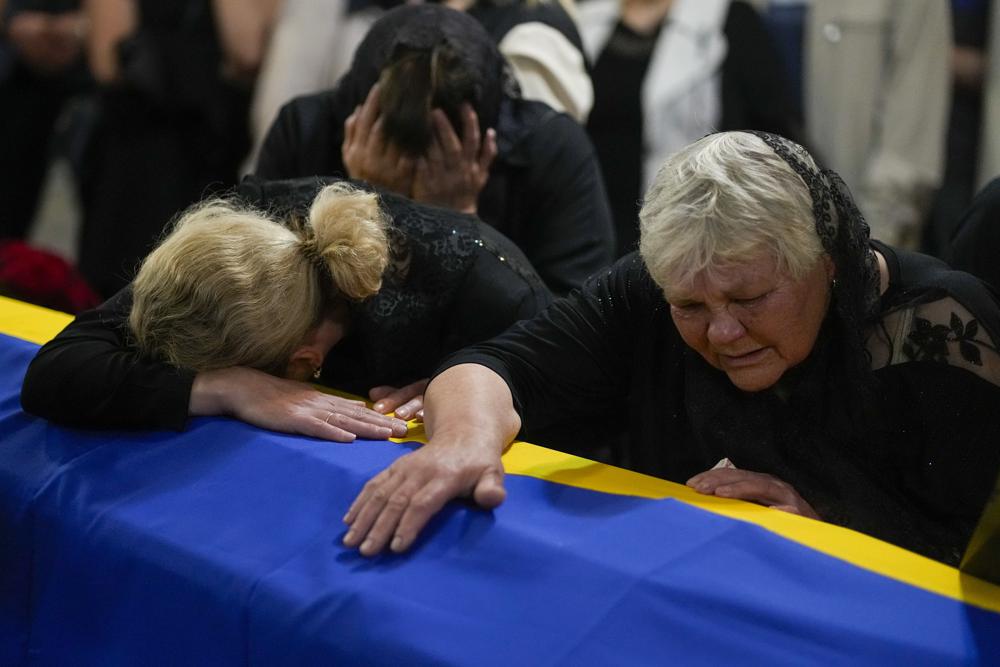
The mother, right, and sister of Army Col. Oleksander Makhachek mourn over the coffin with his remains during a funeral service in Zhytomyr, Ukraine, Friday, June 3, 2022. According to combat comrades Makhachek was killed fighting Russian forces when a shell landed in his position on May 30. (AP Photo/Natacha Pisarenko)
When Vladimir Putin sent troops into Ukraine in late February, the Russian president vowed his forces would not occupy the neighboring country. But as the invasion reached its 100th day Friday, Russia seemed increasingly unlikely to relinquish the territory it has taken in the war.
The ruble is now an official currency in the southern Kherson region, alongside the Ukrainian hryvnia. Residents there and in Russia-controlled parts of the Zaporizhzhia region are getting offered Russian passports. The Kremlin-installed administrations in both regions have talked about plans to become part of Russia.
The Moscow-backed leaders of separatist areas in eastern Ukraine’s Donbas region, which is mostly Russian-speaking, have shared similar intentions. Putin recognized the separatists’ self-proclaimed republics as independent states two days before launching the invasion. Fighting has intensified in Ukraine’s east as Russia seeks to “liberate” all of the Donbas.
The Kremlin has largely kept mum about its plans for the cities, towns and villages it has bombarded with missiles, encircled and finally captured. Spokesman Dmitry Peskov said it was up to people living in seized areas to decide where and how they want to live.
Peskov told reporters Friday that Russian forces have “liberated” parts of Ukraine and “this work will continue until all the goals of the special military operation are achieved.”
In a video message marking the war’s first 100 days, Ukrainian President Volodymyr Zelenskyy indicated that his country would not submit easily to Russian aggression after showing it could withstand months of attacks from a larger adversary.
“We have defended Ukraine for 100 days already. Victory will be ours,” he said.
Annexing more land from Ukraine was never the main goal of the invasion, but Moscow is unlikely to let go of its military gains, according to political analysts.
“Of course (Russia) intends to stay,” Andrei Kolesnikov, senior fellow at the Carnegie Endowment for International Peace, said. To Russia, “it’s a pity to give away what has been occupied, even if it was not part of the original plan.”
Putin has said the invasion was aimed at the “demilitarization” and “denazification” of Ukraine. It was widely believed that the Kremlin intended initially to install a pro-Moscow government in Kyiv that would prevent Ukraine from joining NATO and other steps away from Russia’s sphere of influence.
Russia captured much of Kherson and neighboring Zaporizhzhia early in the war, gaining control over most of Ukraine’s Sea of Azov coast and securing a partial land corridor to the Crimean Peninsula, which Russia annexed from Ukraine in 2014. They completed the takeover last month with the capture of the port city of Mariupol following a three-month siege.
Residents of the cities of Kherson and Melitopol took to the streets to protest the occupation, facing off with Russian soldiers in plazas. Ukrainian officials warned that Russia might stage a referendum in Kherson to declare the region an independent state.
Petro Kobernyk, 31, an activist with a nongovernmental organization who fled Kherson with his wife, told The Associated Press that Russian security services threatened and held pro-Ukrainian activists or forced them out of the region.
His claims could not be independently verified. Russian forces keep people in an “an information vacuum,” with Ukrainian websites no longer available, Kobernyk said.
He described a bleak life in Kherson. With many stores shut down, the city “has turned into an endless market where people exchange goods for medicines and food.”
But some in captured areas of Ukraine have welcomed a Russian takeover. Vadim Romanova, a 17-year-old from Mariupol, said it made one of his dreams come true.
“I’ve wanted to live in Russia since I was little, and now I realize I don’t even have to move anywhere,” Romanova said.
In Russian-occupied cities in southern Ukraine, people with pro-Kremlin views replaced mayors and other local leaders who disappeared in what Ukrainian officials and media said were kidnappings. Russian flags were raised, and Russian state broadcasts that promoted the Kremlin’s version of the invasion supplanted Ukrainian TV channels.
The Russian ruble was introduced as the second official currency in both the Kherson and Zaporizhzhia regions — at least in the parts under Russian control — and pro-Russian administrations started offering a “one-time social payment” of 10,000 rubles (roughly $163) to local residents.
An office of Russia’s migration services opened in Melitopol, taking applications for Russian citizenship through a fast-track procedure Putin expanded to residents of the captured southern regions. The rapid procedure was first implemented in 2019 in the rebel-controlled areas of the Donbas, where more than 700,000 people have received Russian passports.
Top Russian officials started touring the regions, touting the territories’ prospects for being integrated into Russia. Deputy Prime Minister Marat Khusnullin visited Kherson and Zaporizhzhia in mid-May and indicated they could become part of “our Russian family.”
A senior official in the Kremlin’s ruling United Russia party, Andrei Turchak, put it even more bluntly in a meeting with residents of Kherson: “Russia is here forever.”
Members of the pro-Kremlin administrations in both regions soon announced that the areas would seek to be incorporated into Russia. While it remains unclear when or if it will happen, Russia is laying the groundwork.
Oleg Kryuchkov, an official in Russia-annexed Crimea, said this week that the two southern regions have switched to Russian internet providers; state media ran footage of people lining up to get Russian SIM cards for their cellphones. Kryuchkov also said that both regions were switching to the Russian country code, +7, from the Ukrainian +380.
Senior Russian lawmaker Leonid Slutsky, a member of the Russian delegation in stalled peace talks with Ukraine, said that referendums on joining Russia could take place in the Donbas, Kherson and Zaporizhzhia regions as early as July.
Kremlin spokesman Peskov was evasive when asked Friday whether Russian authorities planned to hold votes in those areas, saying that it would depend on the course of Russia’s offensive.
Tatyana Stanovaya, founder and CEO of R.Politik, an independent think tank on Russian politics, thinks Putin doesn’t want to rush the referendums and run the risk of them being denounced as shams.
“He wants the referendum to be real, so that the West can see that, indeed, Russia was right, the people want to live with Russia,” Stanovaya said.
Ukrainian experts say it will not be easy for the Kremlin to rally genuine support in Ukraine’s south.
Volodymyr Fesenko, of the Kyiv-based Penta Center think tank, said most residents of the southern regions identify as Ukrainians much more strongly than the people in areas closer to Russia or have been led by the Moscow-backed separatists for eight years.
Olga Romanova, a hairdresser in Mariupol, told the AP she wonders if Ukraine’s people “deserved the war,” if they were somehow being punished for not displaying enough solidarity during the 8-year separatist conflict in eastern Ukraine that preceded the invasion.
Romanova is now sharing her basement with her neighbors to use as a bomb shelter, And even though her son dreams of becoming Russian, she said Ukrainians are clear about what transpired on their land in the past 100 days no matter the Kremlin’s rhetoric.
“Whatever they want to call this combat activity – special operation, defensive, offensive – whatever they want to call it, it was war,” she said. “It was war, and people were dying, buildings were being destroyed, a city was being destroyed. A city where somebody was happy once.”
Copyright 2021 Associated Press. All rights reserved.
























You must be logged in to post a comment Login