The SOVA Android banking trojan continues to evolve with new features, code improvements, and the addition of a new ransomware feature that encrypts files on mobile devices.
With the latest release, the SOVA malware now targets over 200 banking, cryptocurrency exchange, and digital wallet applications, attempting to steal sensitive user data and cookies from them.
Moreover, it features refactored and improved code that helps it operate more stealthy on the compromised device, while its latest version, 5.0, adds a ransomware module.
Rapid evolution
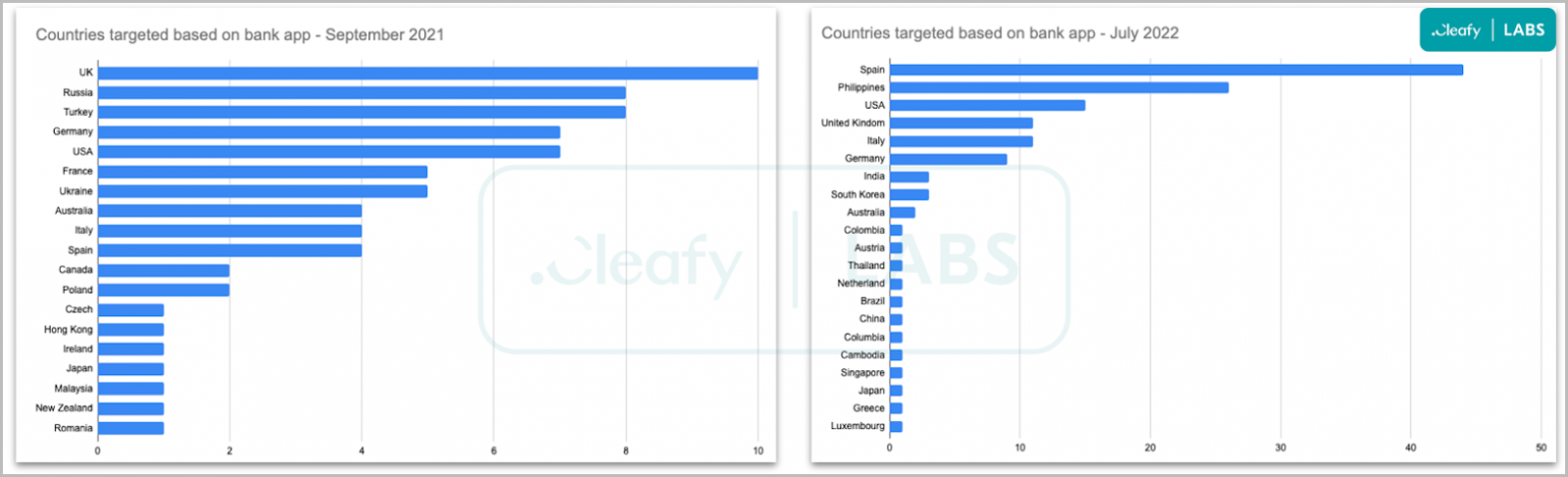
Threat analysts at mobile security firm Cleafy have followed SOVA’s evolution since the project’s announcement in September 2021 and report that its development has rapidly increased in 2022.
In March 2022, SOVA released version 3, adding 2FA interception, cookie stealing, and new injections for multiple banks worldwide. Injections are overlays shown over legitimate login prompts that are used to steal credentials, such as those for online bank apps.
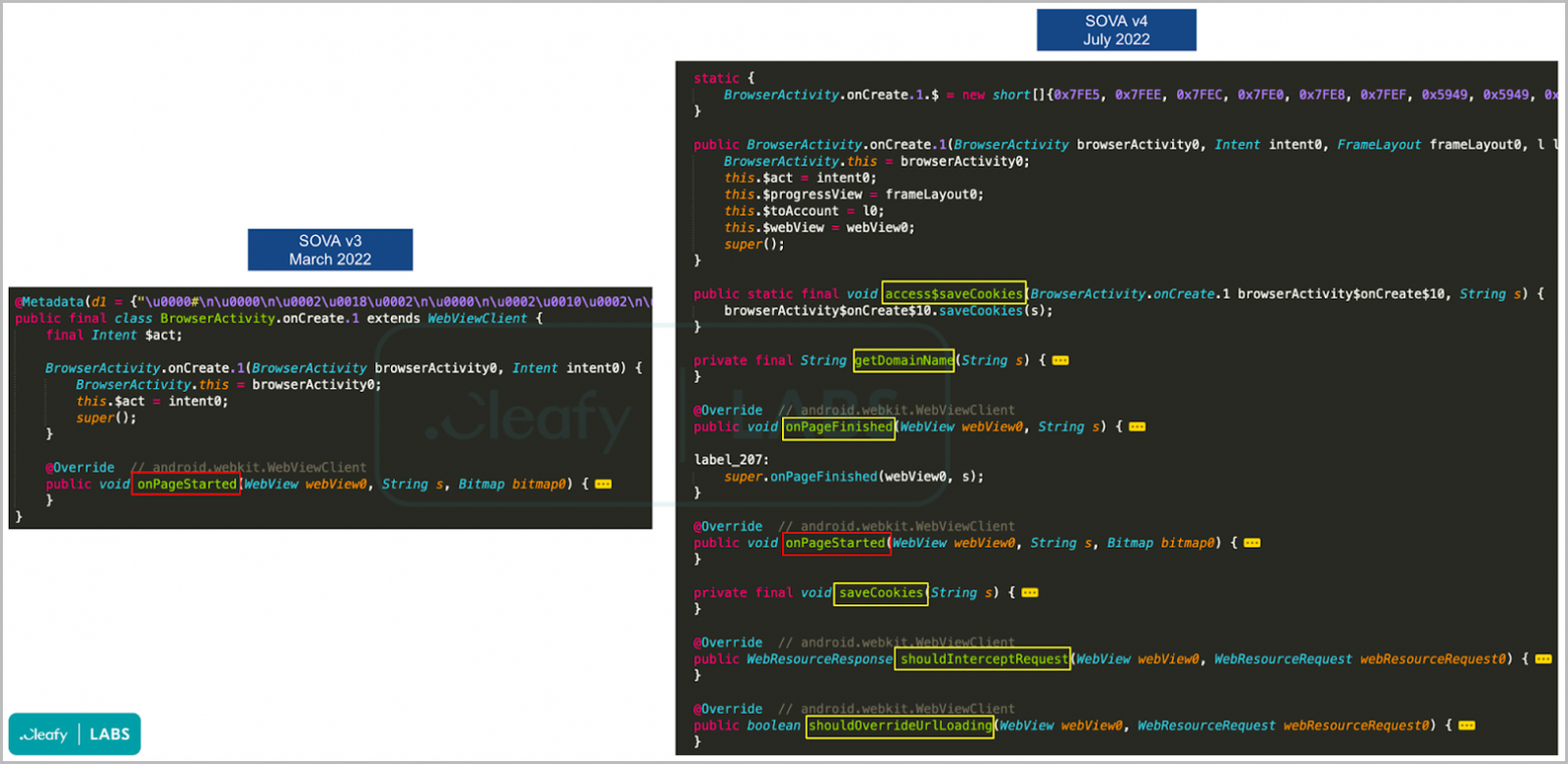
In July 2022, SOVA’s development team released version 4, which took the targeted apps up to 200, and added VNC (virtual network computing) capabilities for on-device fraud.
The malware sends a list of installed applications to the C2 and receives an XML containing a list of addresses that point to the correct overlays to be loaded when the victim opens a targeted app.
The fourth major version also added support for commands such as taking screenshots, performing clicks and swipes, copying and pasting files, and serving overlay screens at will.
This release also saw a significant code refactoring in the cookie stealer mechanism, now targeting Gmail, GPay, and Google Password Manager.
SOVA v4 added some protections against defensive actions, abusing Accessibility permissions to push the user back to the home screen if they attempt to uninstall the app manually.
Finally, the fourth version focused on Binance and the platform’s ‘Trust Wallet’ app, using a dedicated module created to steal the user’s secret seed phrase.
New ransomware module
More recently, Cleafy sampled an early release of SOVA v5, which comes with numerous code improvements and the addition of new features such as a ransomware module.
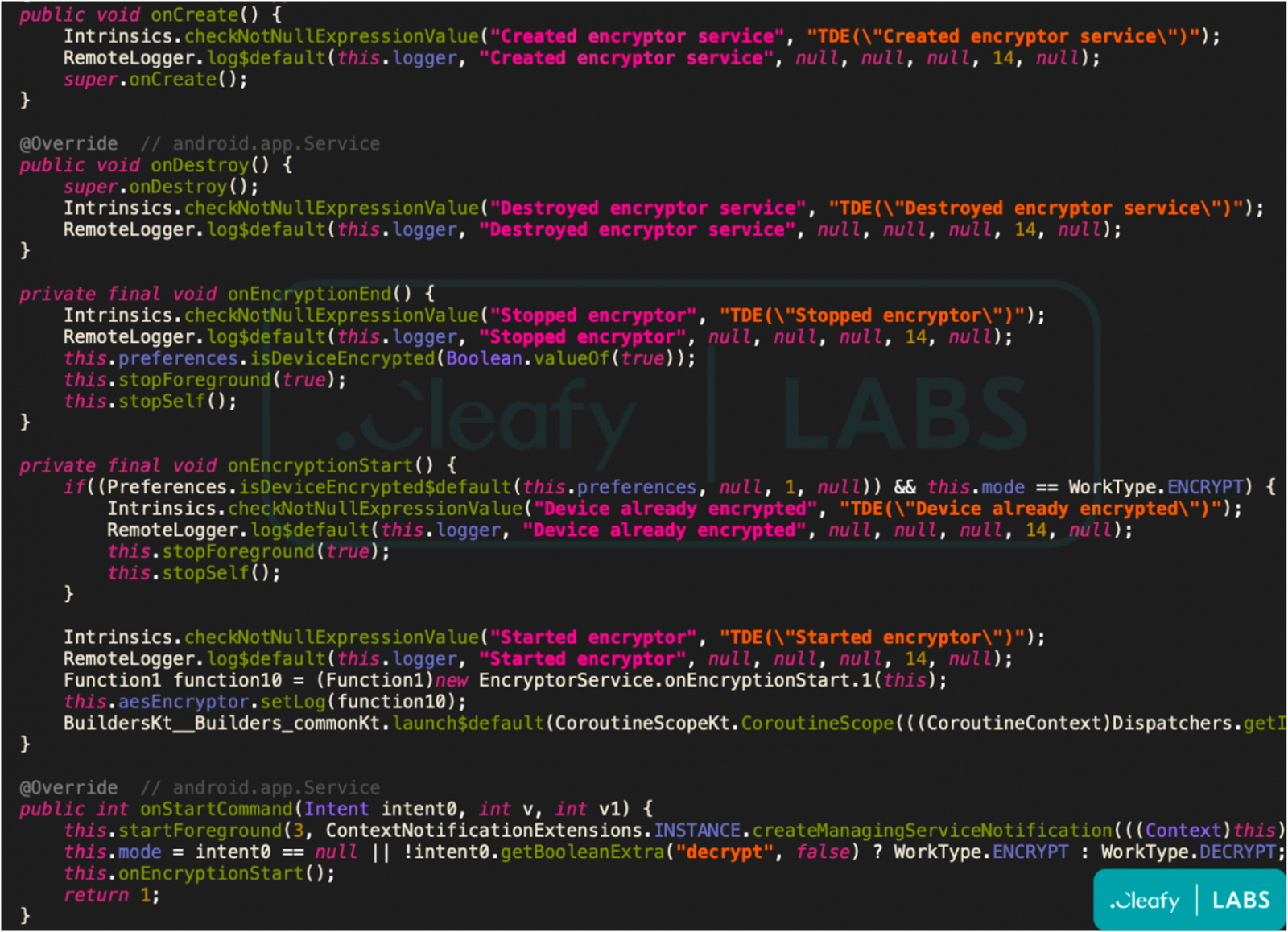
The module uses AES encryption to lock all files in infected devices and append the “.enc” extension on the renamed, encrypted files.
“The ransomware feature is quite interesting as it’s still not a common one in the Android banking trojans landscape. It strongly leverages on the opportunity arises in recent years, as mobile devices became for most people the central storage for personal and business data.” – Cleafy
The fifth version isn’t widely circulated yet, though, and its VNC module is missing from the early samples, so it’s likely that this version is still under development.
Even in its current, unfinished form, SOVA v5 is ready for mass deployment, according to Cleafy, so vigilance is advised to all Android users.
Finally, the malware’s author appears determined and capable of fulfilling their September 2021 promises, sticking to the development timeline and adding advanced features every few months.
This makes SOVA a threat of growing intensity, as the banking trojan is now setting itself as one of the pioneers of the still under-explored space of mobile ransomware.




























You must be logged in to post a comment Login